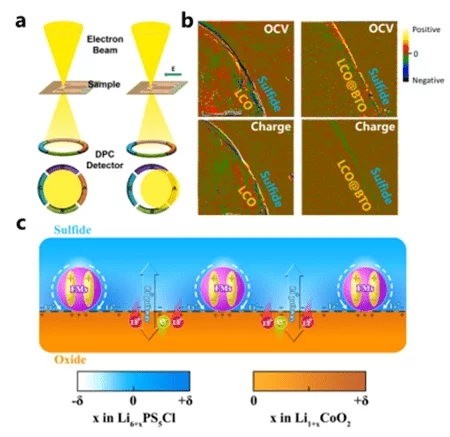
From the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Processes, Chinese Academy of Sciences (QIBEP), we have learned that Researcher Guanglei Cui and Associate Researcher Jun Ma of QIBEP, in collaboration with Dr. Chao Li and Prof. Jun Luo of Tianjin University of Science and Technology (TUST), and Researcher Lin Gu of the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOPC), have achieved the first visualization study of the lithium transport at the lithium cobaltate/sulfide electrolyte interface by using in situ scanning transmission electron microscope (ISTEM) differential phase-lining imaging, and have also demonstrated that it is feasible to improve the interfacial lithium transport at the interface by designing and preparing By designing and preparing the interfacial structure with discontinuously distributed barium titanate (BaTiO3 ) nanosingle crystal particles, the feasibility of a novel coupling technique of built-in electric field and chemical potential to improve the interfacial lithium transport has been demonstrated, which provides a new technological solution to improve the interfacial lithium transport and to enhance the fast-charging performance of batteries.
In addition, based on the above research progress, the team has deepened the understanding of the key scientific issues of sulfide solid-state batteries from the perspectives of supramolecular chemistry and interfacial conformational relationships, and has provided constructive solutions for the rational design of high-energy-density solid-state lithium-metal batteries and for solving the technological bottlenecks in them.
(Sources: Energy Scholar, China Science Daily, China Youth Daily, Shanghai Institute of Silicate Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences)
[Zhongshun New Energy Marketing Department December 8, 2020 Responsibility: Xiao Zheng]
* Reproduced for the purpose of transmitting more information, and does not mean that we endorse its views and are responsible for its authenticity.




